Tomorrow morning, we will pull ourselves together and make slow ascent up Bald Peak, the first leg in our voyage to Hillsdale. Hope to see you all there after the 10:00 AM opening bell.
 PreservesPreserve production is when we reprise our summer, the good moments and the disappointments. All of the fruit we use, with the exception of lemons, comes from the farm. Many farmers contemplate preserve production as a way to capitalize on surpluses and low grade fruit, throw some sugar and pectin into a big pot and you have something to sell. Extension people call it "value-added." As we warn other farmers, the notion that making preserves is "value-added" is simply poppycock. We must purchase the jars, organic sugar, organic lemons and pay for the use of Sweet Creek's kitchen and staff. We have added an investment and value is added only if and when you sell the preserves for a profit, so there is no sense poking some low grade fruit in glass.
PreservesPreserve production is when we reprise our summer, the good moments and the disappointments. All of the fruit we use, with the exception of lemons, comes from the farm. Many farmers contemplate preserve production as a way to capitalize on surpluses and low grade fruit, throw some sugar and pectin into a big pot and you have something to sell. Extension people call it "value-added." As we warn other farmers, the notion that making preserves is "value-added" is simply poppycock. We must purchase the jars, organic sugar, organic lemons and pay for the use of Sweet Creek's kitchen and staff. We have added an investment and value is added only if and when you sell the preserves for a profit, so there is no sense poking some low grade fruit in glass.
We started making preserves from the opposite end of the harvest. The very first berries to ripen in the field are the highest quality fruit. They set up well without any added pectin and the flavor is brightest due to their higher acidity. For us, taking the better part of the day to deliver ten flats of berries is a waste of time and fuel. So early in the morning, we bring in a few flats each day and freeze the berries. We never crush them; they are packed into buckets whole when frozen. This gentle treatment preserves the aromatics and acidity of the fruit, as many of you know because you handle our berries the same way.
Our preserves are very farmer-ish, just one type of fruit and no secret ingredients or surprising combinations. The preserves are cooked in 2½ gallon steam jacket pots, so the cooking surface is a gentle 270°F (132°C). We cook about a gallon at a time. Paul Fuller has three 275-gallon pots, but at that volume, you have to add pectin in order for the fruit to gel. Several years ago, Carol's brother, Bill, visited the farm and walked us through a series of very carefully documented variations. Tasting the various versions, it was clear to us that adding pectin robbed a vital part of the fruit's spirit, inconvenient and indisputable. Sweet Creek has just two of these small pots, but Paul is adding two more so we can increase production next year. There is no other co-packer in Oregon that would put up with our fussy demands, so as long as Paul and Judy own Sweet Creek welcome us back, we will make preserves.
The most important tool for us is Paul's Omega HH1501AJK digital thermometer. In cooking, the fruit goes through a series of temperature steps. The critical range is 220 to 222°F (104.4 to 105.5°C). The fruit sets up in that range, if you allow it bounce up to 224°F (106.6°C) the fruit has an over-cooked flavor and texture. One year, the cord to the thermometer frayed and we had to use a different one for the last run of the day. The calibration was off and the fruit over-cooked slightly. We now have our own Omega, so if one goes we have a back-up. It also allows us to conduct test runs at home.
As we noted earlier, we see the season reflected in the fruit. The heat wave that came through during our ramble in June destroyed much of the black currant, boysenberry and blackcap crop. We have some, not enough to for the stores. The early raspberry and loganberry crops preceded the heat wave, so they are in good supply. We have done an even better job with the tart cherry preserves, though they are inherently lower in pectin than other fruit and on the runny side. We have yet to perfect pit removal, so there will be an occasional pit in the jars. This preserve is an even greater labor love than the others and we should drop it but we like too much. This year, we have added a small run of grape preserves from the Veepie grape. The goal is a grown-up grape flavor with skins in the mix. The golden gage and mirabelle are back as well.
Speaking of labors of love, Aphrodite is often portrayed holding a quince. Our two small quince trees had such a heavy crop that the trees largely collapsed. We have a small run of quince jelly in memoriam for the efforts of those two unfortunate trees. They will recover eventually and we are planting more because we cannot imagine life without a bit of quince jelly. Eventually, we will add more jellies to the mix. We have several crab apples which should bear good crops in a year or two. The jellies will test Paul's patience even more, which should him some level of beatification among fruit lovers. Though we promise him that we will stop at 19 different preserves, a good prime number, so there are just two more types to go.
In addition to our 17 different fruit preserves, we will have a good supply of beans for the next two markets, as well as Roy's Calais Flint cornmeal and kernels for hominy. No popcorn yet, needs more time to dry.
We will also have a good selection of greens, including sorrel, which is virtually the same as lengua de vaca, the type of sour dock green used in traditional posoles. Kathryn will be demonstrating the fine points of posole construction at this week's market demonstration.
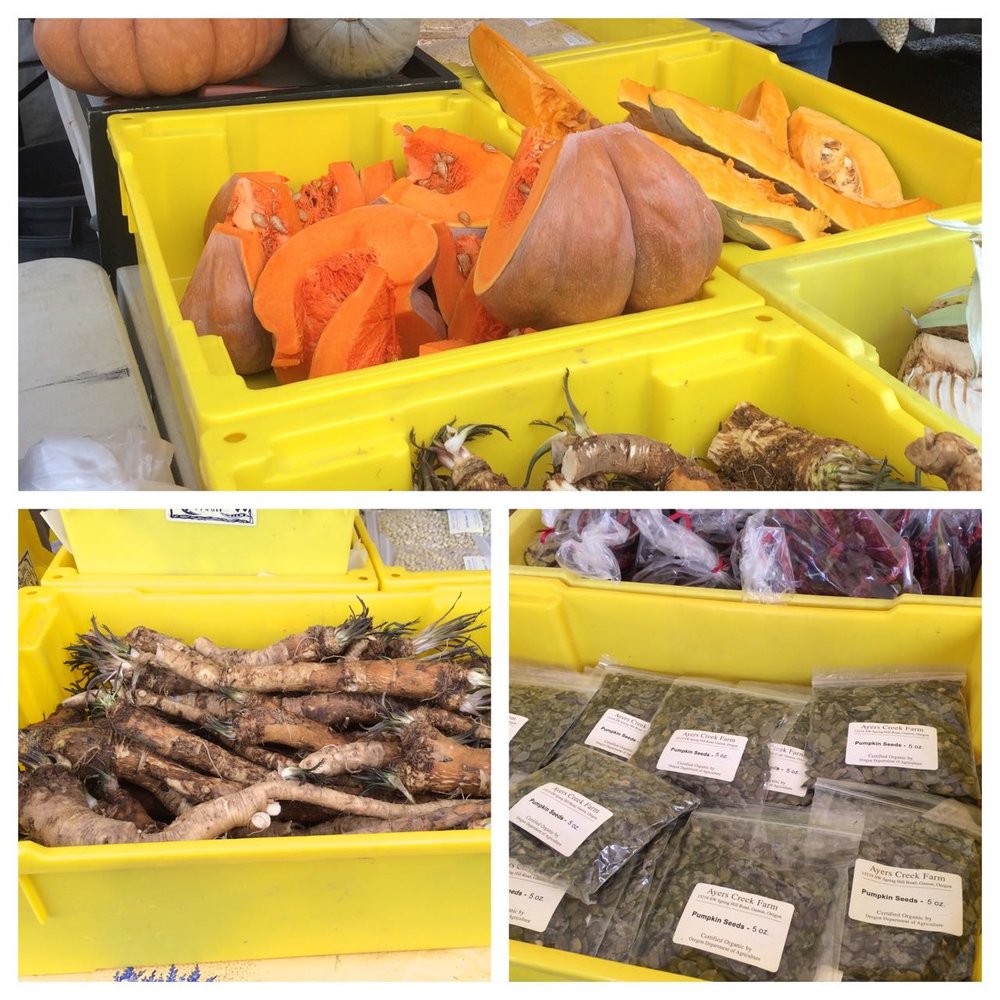
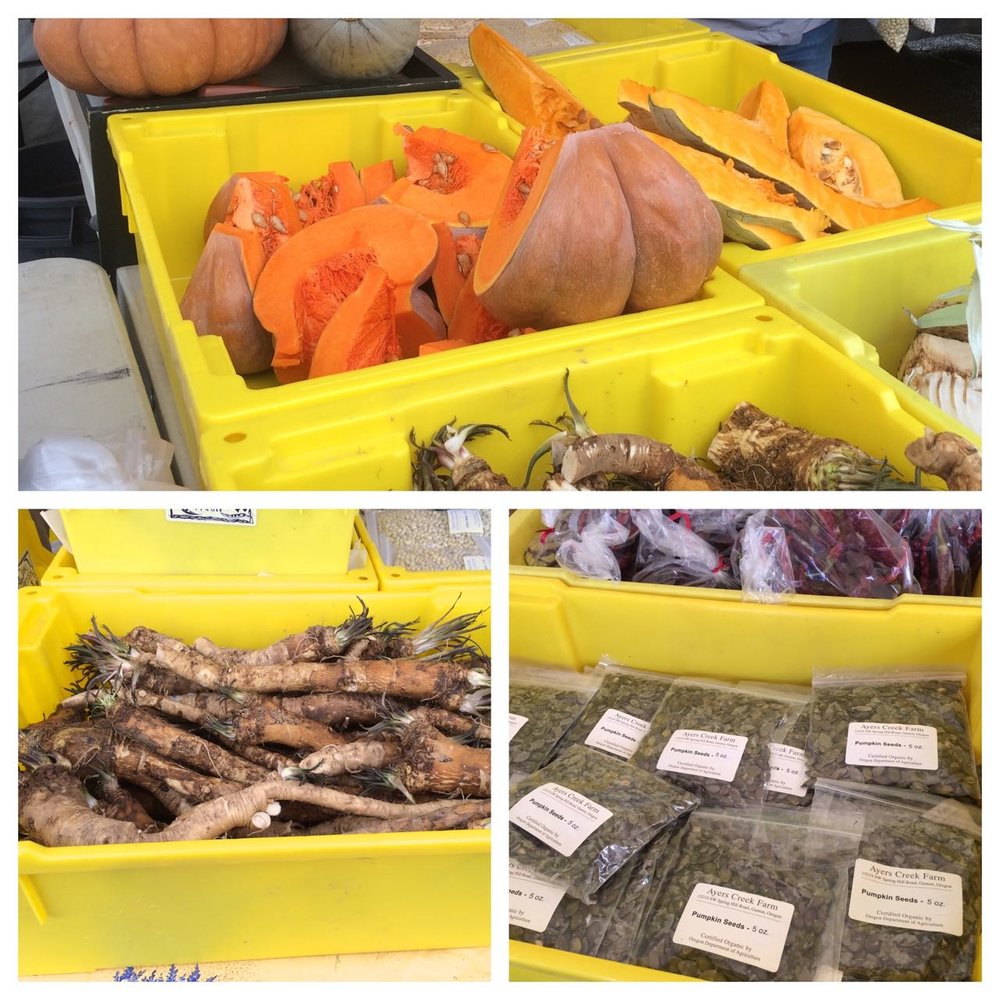
Winter squash has cured nicely and we will also bring in ash gourds, also known as winter melon, for the first time.
The cayenne peppers, Joe's Long and Aci Sivri are ready.
The roots include Yellow Finn spuds, knob celery, black radish, beets and the star of the farm, fresh horseradish. For those disposed towards a libation with Sunday brunch, imagine a Bull Shot or Bloody Mary with good dose of freshly grated horseradish. Might not even need the vodka to enjoy such a fine beverage. The salad and seafood are also improved with a grating of horseradish.
Finally, we will have some chestnuts. Remember, you have to pierce the shell to let the steam escape. There is no need to make a cross unless you want to, a slit is sufficient. When the chestnuts have finished roasting, generally when the kitchen smells like roasting chestnuts, put them in a bowl lined with a wet dishcloth. Cover and let them rest for a few minutes, and then shell while they are still hot. The task is easiest when it is a painful experience. If they get cold, the pelicle or inner skin, is harder to remove. Chestnuts are perishable, difficult to use once they dry. We cure them in our root cellar at 90% humidity where the sweeten up, they will last a few days on the counter, or longer in the refrigerator.
Enough, we will see you all tomorrow.
Carol & Anthony
Ayers Creek Farm